Lean Factory Audit (LFA) to benchmark manufacturing excellence in production, processing, warehouse, logistics, and laboratory against world-class references.
How mature is your industrial operation? With the Factory Audit, you can measure leanness against world-class manufacturing standards and practices. The online audit is for operations executives, factory managers, consultants and investors to define the current state of reality, assess working conditions, verify compliance with good manufacturing practices (GMP), provide direction for improvement efforts and collect data for Lean Manufacturing Certification and factory acceptance testing. The outcome of the Lean Manufacturing Assessment also serves as a benchmark on the path to the Smart Factory.
Cases, when to use it:
- Lean manufacturing benchmarks not known
- Gap to world-class manufacturing not defined
- Complacency, lack of improvement, “fat & happy”
- Unclear strategy to achieve the smart factory
Clients, for whom it is:
- Operations directors, factory managers
- Consultants and improvement champions
- Investors and owners of industrial operations
- For anyone to measure leanness and maturity
Process, how it works:
- Lean factory audit to answer 126 questions in 2 hours
- Challenge status quo by measuring against world-class
- Identify strengths and improvement opportunities
- Learn about Lean benchmarks, best manufacturing practices
Benefits, what to gain:
- Manufacturing excellence level on a 5-point scale (free)
- Inspiration and insights to develop better improvement plans
- Detailed assessment report with best practices (purchase)
- Progress measurement for Lean manufacturing certification
The Lean Factory Audit Measures Operational Maturity, the Degree of Manufacturing Excellence
The Lean manufacturing assessment tool is used by a wide range of companies, such as automotive assembly plants, pharmaceutical manufacturers, medical laboratories, semiconductor fabs, electronic and appliance factories, and logistics operations. The factory audit gives companies the key information about how their operation compares to the best-in-class (BIC). The assessment framework is suitable for all operation configurations, from projects, job shops, flow shops, line flow, to continuous flow. The product-process matrix below helps auditors to classify manufacturing operations in preparation for the audit.
Product-Process Matrix to Classify Manufacturing Operations by Volume and Standardization vs Variety and Customization
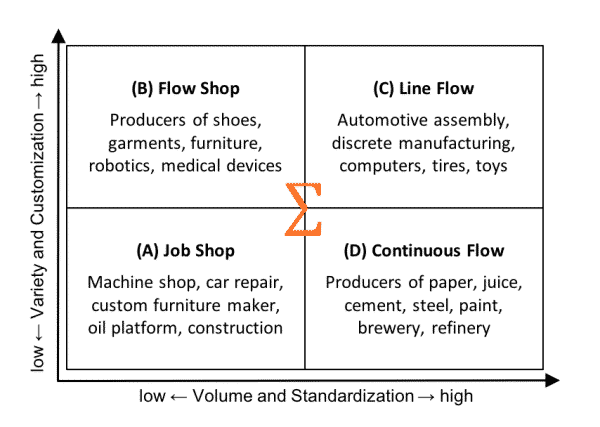
X: Project to produce a unique item in a flexible project configuration, such as paving a road, building a pipeline, or engineering a spacecraft.
A: Job Shop to process similar jobs in a jumbled flow or job-shop configuration, such as in a print shop, tooling shop, repair shop, or carpenter’s work shop.
B: Flow Shop to process batches in disconnected-line flow or in a flow-shop for producing bread, shoes, garments, furniture, or medical devices.
C: Line Flow for repetitive manufacturing in connected lines for the assembly of computers, cars, suitcases, tires, toys, and household appliances.
D: Continuous Flow for uninterrupted production of a single product (no mix), such as oil, cement, steel, pasta, beer, granulates, paper.
The Lean Factory Audit Framework is Based on The 20 Keys to World-Class Manufacturing (WCM)
The Lean factory audit is a gap-fit analysis and manufacturing benchmarking tool that can be used by any factory or supply chain organization to evaluate health and maturity based on 20 categories. The two diamond marked categories – Inventory* and Maintenance* – are specific to the factory audit, while all other 18 keys are the same for the Lean Factory and Lean Office assessment. After answering 126 questions, you will receive your evaluation report so make sure you are logged in to receive your results via email → Register & Login → return to this page to start with lean questionnaire.
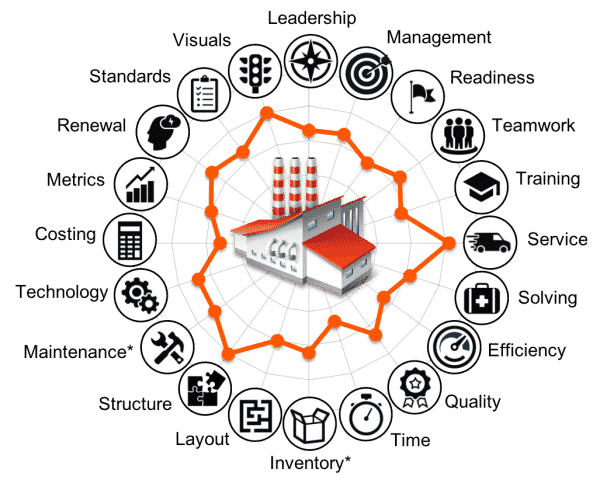
- Costing and budgeting, process and system.
- Efficiency management and resource planning.
- Inventory* amount and management system.
- Layout, distances, communication, ergonomics.
- Leadership and policy deployment process.
- Maintenance* and asset management.
- Management, priority setting, decision making.
- Metrics and performance measurement.
- Quality level, process capability, yield.
- Readiness, willingness to change, flexibility.
- Renewal, innovation and improvement.
- Service level, internal and external customers.
- Solving, root-cause analysis and elimination.
- Standards, policies, procedures, instructions.
- Structure, organizing and housekeeping, 5S.
- Teamwork, cooperation and coordination.
- Technology, equipment, computers, systems.
- Time management, deadlines, commitments.
- Training, capability building, skill flexibility.
- Visuals, status signals, visual management.
The manufacturing assessment checklist is free, so you can measure status and progress anytime. After answering 126 questions, you will receive your factory evaluation report, so make sure you are logged in to receive your results via email (→ Login ). The assessment data are fully protected (→ Privacy ) and reports are stored in your account and only accessible by you (→ Audits ). The only information we collect is anonymous summary statistics, such as the median manufacturing excellence level by industry and country. So, get started now by setting the baseline for Lean Manufacturing.
The 20 Keys to World-Class Manufacturing Are the Foundation for a Smart Factory
Key-01: Costing
To set optimal prices and make bottom-line oriented decisions requires a solid understanding of costs. Costing involves collecting and classifying costs that occur while carrying out an activity or accomplishing a purpose. This also includes allocating expenditures to different functions or various stages of a process. Budgeting, which is closely related to costing, is the process of translating quantified resource requirements for capital, people and materials into time-phased goals and milestones. The Lean Audit assesses how well costs are defined, allocated, and controlled. Relevant concepts include the budgeting process, costing system, cost drivers, reviews and controls, accounting of non-performance cost and the cost of poor quality.
Key-02: Efficiency
Efficiency refers to the degree resources used to produce economic value; it is an organization’s ability to deliver products that meet customer requirements—in terms of functionality, quality, and service level—while consuming minimal resources. The factory maturity assessment evaluates how time, money, people, and energy are used for the intended purpose. Efficiency concepts relevant for operational excellence include resource conservation, value generation, waste reduction, efficiency controls, overall equipment efficiency (OEE) and overall process efficiency (OPE), throughput rate and level of production, flow of material and information, quick setups (SMED) and rapid changeover techniques (RCO), factory streamlining, and plant complexity reduction.
Key-03: Inventory
Inventory refers to materials and information held for later use, controlled by inventory management processes and systems that ensure availability at minimal cost of capital. The auditor evaluates inventory structure, method of organization, degree of standardization, limits and controls, classification of items, amount of buffers and safety stocks relative to demand, replenishment triggers and process, sequence of withdrawal, vendor inventory, items in-queue versus work in process (WIP), degree of separation, obsolescence rate, the production process chain, handling and internal logistics, and how overproduction is addressed. Concepts include days of sales in inventory (DSI), flow versus batch process, pull versus push method, and economical batch sizes (EBS).
Key-04: Layout
Layout refers to the way assets are arranged to support people and machines as they perform work in a safe and efficient way. The audit evaluates the flow from raw material to finished good, effectiveness of the manufacturing facility layout, ergonomic aspects of the workstation design, and interactions between operators, machines, systems, suppliers, customers, and the operating environment. The auditor evaluates working conditions, configuration of spaces, asset waste, effectiveness of walk-pattern, the time it takes to fetch parts and information, degree of continuous flow, and how people exchange information. Concepts include the lean plant layout, cellular versus functional concepts, multi-machine handling, distances and transportation waste, workstation ergonomics and motion waste, interactions between people, supplier, customer, and the ease of communication, traffic pattern analysis and flow optimization, level of transparency and conditions for visual management.
Key-05: Leadership
Leadership is a process of using social influence to maximize the efforts of others towards achieving of a goal. It involves making strategic decisions, organizing a group of people, and inspiring them to perform. When assessing leadership as an activity, there are timing implications to understand since the leader might chose to trade short-term gains for long-term benefits. There are also soft factors to consider that are hard to measure, such as influence and inspiration. For the purpose of the leadership assessment, we focus on business strategy, the strategic development framework and the policy deployment roadmap. Concepts include values, orientation, vision, mission, strategy, actions, prioritization, and feedback.
Key-06: Maintenance
The goal of maintenance is to prevent breakdowns and to increase reliability and equipment life so factories can run at maximum efficiency. The maintenance checklist assesses how well facility and production equipment is maintained and uptime controlled, and the ability of machines to run at zero unplanned downtime. Concepts include equipment utilization versus availability, production downtime tracking, efficiency ratios, planned versus unplanned stoppages, response process, downtime analysis, machine performance data, maintenance strategies (corrective, preventive, risk-based, conditional, autonomous), maintenance tasks and ownership, as well as maintenance process, system, and service levels.
Key-07: Management
Management refers to the organization and coordination of resources to attain defined objectives in the best possible way. It involves organizing, planning, resourcing, measuring, directing, controlling, and correcting. The Lean Audit evaluates performance management, i.e. how effectively processes and behaviors are managed to ensure compliance and safety, and to achieve desired results. Concepts include planning and decision-making processes, effectiveness of actions, priorities and incentives, performance reviews and feedback, and cross-functional interactions.
Key-08: Metrics
Metrics are standards of measurement to evaluate the performance or progress of a plan, process, product, project, or person against known standards of accuracy, completeness, speed, or cost. The Lean Audit assesses the effectiveness of the measurement process and system. Concepts include goal alignment, key performance indicator, balanced scorecard, measurement process, and performance reviews (scrum).
Key-09: Quality
Quality is a measure of excellence or a state of being free from defects, deficiencies, and significant variations. It is achieved by strict and consistent commitment to established standards that drive uniformity in a product or processes to satisfy the customer’s specification, expectation, or user requirement. The factory quality assessment measures the factory’s ability to deliver goods and services that are “fit for purpose”, the level of quality designed into products and supply chain to meet market expectations. Concepts include process variability, sigma level, quality organization, quality assurance testing and inspection, quality controls, mistake proofing, process capability, yield and defect rate, quality-driven costs, quality culture, and the maturity of the quality management system overall.
Key-10: Readiness
Readiness refers to the state of preparedness needed to face and implement change. It involves having a vision and resources in place, engaging people, and creating the motivation to act. Readiness is strongly influenced by the thoroughness of planning, adequacy of training, and availability of support services. The Lean Audit assesses how prepared an organization is to adapt to (a) advances in technology, (b) a shift in customer preferences, and (c) changes in the competitive landscape. It scores awareness and openness towards change, attachment to the status quo, the sense of urgency, the capacity to lead change, the overall change culture and its ability to drive continuous improvement.
Key-11: Renewal
Continuous improvement to drive perpetual renewal is a prerequisite for sustaining success in the marketplace; it allows an organization to maintain continuity in a discontinuous operating environment. The Lean Audit evaluates an organization’s ability to renew itself, to continually create more effective strategies, structures, products and services based on the premise that different is not necessarily better, but better is always different. Concepts for evaluating renewal include factory improvement, product innovation, and management intervention.
Key-12: Service
A service is a type of economic activity that is intangible, cannot be stored, and does not result in ownership. A service is consumed at the point of sale. Services are one of the two key components of economics, the other being goods. Examples of services include the transfer of goods, such as shipping products or delivering mail, and the application of knowledge by a teacher, doctor, or consultant. Service level is a measure of responsiveness to meet customer requirements, making it a key performance indicator for essentially all businesses. The Lean Factory Audit assesses delivery performance to internal and external customers, capability of service processes, expectations versus needs, customer service and satisfaction levels, service quality references, service level agreements, vendor capability and capacity, and net promoter score.
Key-13: Solving
Problem solving is the process of correcting a deviation from a standard or target, or closing the gap between the initial state and the desired state. The auditor assesses the effectiveness of the problem solving process and quality system, and how well problems are addressed and solved. Concepts include abnormality detection, problem solving skills and processes, speed of intervention, root cause elimination, corrective versus preventive action, testing solutions, problem solving effectiveness and re-occurrence rate.
Key-14: Standards
Operational excellence standards capture current best practices, define the manufacturing process and right way of working (WOW), while establishing a baseline for improvement. The Lean Audit assesses to which degree processes follow standards and the effectiveness of procedures to ensure predictable outcomes. Concepts include accessibility of standards, procedure quality, capability maturity model, content and controls, usefulness to guide workers and managers, update frequency, and link between standards and continuous improvement process.
Key-15: Structure
Structure is the foundation of a safe, efficient workplace. The Lean Audit assesses organizational level based on the 5S concept that a place is defined for each item and all items are kept at their defined places. The auditor looks at the general appearance and cleanliness of the workplace, organizational standards, training and 5S knowledge, abnormality tagging, 5S checklists, housekeeping process, discipline to standards, feedback frequency, degree of deployment and 5S system coverage.
Key-16: Teamwork
Teamwork refers to people working together toward a common goal, sharing ideas, transferring knowledge, and balancing the workload among members. Teamwork is an outcome when activities require more capacity or capability than a single person can provide, or when synergies among team members create more benefits than the sum of individual contributions. People working in teams with a clear purpose and good chemistry not only improve business results, but they improve engagement and job satisfaction; everybody wins.
Key-17: Technology
Technology refers to the applied knowledge and use of methods, machines, systems, modifications and arrangements to achieve a specific goal or to perform a specific function. For the Lean Audit, we evaluate the purposeful application of knowledge in the design, production, and utilization of goods, the level of digitalization, and the organization of human activities. Concepts include benchmarking of site technology, technical capabilities, engineering prowess, technology readiness level, degree of automation and autonomation, computer-integrated workflow, work allocation and monitoring processes, digital maturity, and progress towards smart manufacturing or industry 4.0.
Key-18: Timing
Time or workload management refers to the effective use of the available time to accomplish a task or job. With conscious use of time, productivity increases as more time is allocated to important tasks, and work is accomplished faster with less time wasted by waiting and idling. The Lean Audit assesses how well activities are planned, and time is used and controlled. Concepts include workload planning and pacing, resource allocation, task prioritization, right first time, takt time, task time, process time, lead time, status and progress tracking, absenteeism and on-time performance.
Key-19: Training
Training refers to an organized activity aimed at imparting knowledge to improve performance or to develop a skill. As part of the human capital management (HCM), the audit evaluates how well people are being trained and prepared for their future roles in the organization. It scores bench strength, skill assessment robustness, quality of appraisals, capability and capacity building processes, degree of continuous learning, effectiveness of coaching and feedback, how training is initiated and delivered, breadth of the training program, quality of the certification process, and how well career development is executed for workers, functional specialists, and leaders.
Key-20: Visuals
Visuals relay information to and between people so they can perform work without the help of papers and computers. Lean companies use visuals to improve speed and efficiency by involving operators in the decision-making process. The Lean Audit assesses to which degree the operation is managed visually, the types of visuals in use, the degree of transparency, visual management, visual processes control, and visual inventory management.

